How is PE plastic manufactured into daily products?
Polyethylene (PE) is by far the most common type of consumer plastic, and is used in many everyday materials. It is a thermoplastic product, which means that it can be melted into a liquid and then cooled back into a solid. Different processing conditions give rise to different grades of polyethylene that can be used for different purposes. PE plastic can appear in our really basic daily products such as plastic bags, water bottles, wires, shoes to other complex things such as delicate parts in vehicles or construction site. In this article, we will find out how PE plastic is used to make plastic items regarding each manufacturing technology.
- What is PE plastic?
Polyethylene consists of hydrocarbon chains with the most basic component being the ethylene molecule, consisting of 2 carbon and 4 hydrogen atoms. When ethylene molecules are combined together in straight or branched chains, polyethylene is formed. This process involves splitting the double bond between the 2 carbon atoms and creating a free radical to join to the next ethylene molecule. The macromolecules are not covalently joined, but are held together in a crystalline structure through intermolecular forces. The lower the number of side branches, the lower the crystallinity and hence the higher the density as can be observed in the differing properties for differing types of polyethylene.
With this molecular structure, PE plastic includes these characteristics:
- Economical
- Low co-efficient of friction
- Excellent chemical resistance
- Stable in cryogenic environments
- Good impact resistance
- FDA/USDA approved
- Resistant to many solvents
- Good fatigue and wear resistance
- Zero water absorption


2. Types of PE plastic and their application
- Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is a very flexible material with unique flow properties that makes it particularly suitable for shopping bags and other plastic film applications. LDPE has high ductility but low tensile strength, which is evident in the real world by its propensity to stretch when strained.

- Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE) is very similar to LDPE, but offers added advantages. Specifically, the properties of LLDPE can be altered by adjusting the formula constituents, and the overall production process for LLDPE is typically less energy-intensive than LDPE.

- High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is a robust, moderately stiff plastic with a highly crystalline structure. It is frequently used in plastic for milk cartons, laundry detergent, garbage bins, and cutting boards.

Main features of each kind of PE plastic are shown in the following table to make it easy to compare:
| Properties | LDPE | HDPE | LLDPE |
| Melting point (°C) | 120-140 | 105-115 | 112-124 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 0.93-0.97 | 0.910-0.940 | 0.917 – 0.94 |
| Tensile strength (MN/m2) | 6.9-15.9 | 21.4-38 | 7.93 – 45.5 |
| Heat distortion temperature (°C) | 40-50 | 60-82 | 75-97 |
| Processability | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Clarity | Near transparent to opaque | Translucent to opaque | Near transparent to opaque |
3. Manufacturing process of PE plastic products
In PE plastic production, nowadays manufacturers apply 4 technology: injection molding, blow molding, extrusion and blown film extrusion. We will find out how familiar PE plastic items are made in factories before being used in human’s life.
3.1. Injection molding
Injection molding is an important technology in manufacturing PE plastic products because many items in our daily life are made from this, such as chair, toys, cutting tools, containers and others. Manufacturing process is more complicated compared to other producing methods, and therefore more expensive.
Molds for injection molding are highly complex and need to be manufactured to tight tolerances to produce high-quality parts. Due to the high temperature and pressures involved, these molds are machined from metals like hardened steel. Softer aluminum molds are less expensive, but also wear faster, so are typically used for more moderate production runs
- Mold setup: If the part has inserts, these are added either by hand or robotically. The mold is closed by a hydraulic press.
- Plastic extrusion: Small plastic pellets are melted and extruded through a heated chamber by a screw.
- Molding: The molten plastic is injected into the mold.
- Cooling and release: The part cools in the mold until it is solid enough to be ejected, either mechanically or by compressed air.
- Post-processing: Sprues, runners and any flash (if applicable) is removed from the part, often automatically as part of the mold opening.


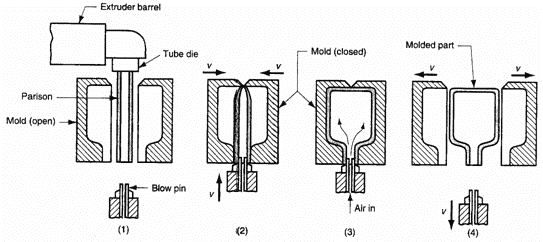
3.2. Blow molding
- Mold setup: Small plastic pellets are melted and formed into a hollow tube, called the parison or preform (depending on the blow molding subtype).
- Molding: The parison is clamped into a mold and gets inflated by pressurized air until it takes the shape of the inside of the mold.
- Cooling and release: The part cools in the mold until it is solid enough to be ejected.
Blow molding operates at far lower pressures than injection molding, which contributes to a lower tooling cost. Much like injection molding and extrusion, blow molding is a continuous process that can be fully automated, resulting in high production rates and low unit costs.
Blow molding is the most common process for creating hollow plastic products at scale. Typical applications include as bottles, toys, automotive components, industrial parts, and packaging.

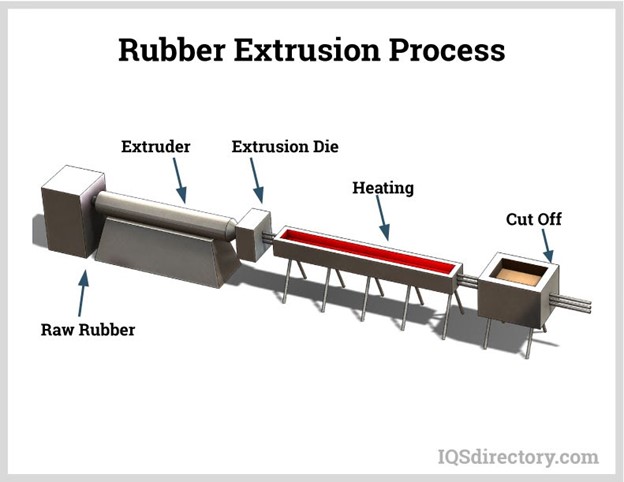
3.4. Extrusion
- Plastic extrusion: Plastic is heated and pushed through a heated chamber by a screw.
- Molding: Plastic is forced through a die that creates the final shape of the part.
- Cooling: The extruded plastic is cooled.
- Cut or spool: The continuous shape is spooled or cut into lengths.
Extrusion machinery is relatively cheap compared to other industrial machines like CNC or injection molding as it is less complex and does not require such high levels of machine accuracy. Due to the simple shapes, dies are also less expensive, with tooling costs that are a fraction of molds for injection molding.
Much like injection molding, extrusion molding is an almost continuous process, which makes the price of extruded parts very low.
Forms and shapes that can be manufactured with extrusion are limited to products that have continuous profiles, such as T-sections, I-sections, L-sections, U-sections, and square or circular sections. Typical applications include pipes, hoses, straws, and window frame moldings.

3.5. Blown film extrusion
The extrusion of plastic melt is done via an annular slit die, generally vertically, for the formation of a thin walled tube. The introduction of air takes place through a hole present in the die’s center for blowing up the tube just like a balloon. The cooling of the hot film is done by the high-speed air ring that blows onto it. This air ring is mounted on the top of die. Then following procedures take place:
- The tube of the film continues its movement upwards till is is passed via nip rolls. Here, the tube is flattened for the creation of “lay-flat” tube of film.
- On the higher output lines, exchange of air (which is available in the bubble) takes place. This is called IBS (Internal Bubble Cooling).
- the film’s tube is created into bags by the process of sealing all across the film’s width along with cutting or perforating.


4. Application of masterbatch in manufacturing process of PE plastic products
In PE plastic production, manufacturers tend to use CaCO3 filler masterbatch, color masterbatch and additives masterbatch such as anti UV, antistatic, anti-block and transparent masterbatch to gain benefits. Besides major advantages of each kind of masterbatch such as cost reduction of filler, color making of color masterbatch and properties enhancing of additives masterbatch, masterbatch also offer following features for final products :
- Increase hardness and durability as well as not losing color and transparency of the product.
- Offer glossy, soft, flexible surface with good water resistance to final products
- Withstand high temperatures (below 230 degrees C) in a short time.
- Raw materials are available from nature, safe, low cost, and easy to use for the production of the plastic industry.
US Masterbatch with more than 10 years experience and the latest production technology supplies various kinds of masterbatch with high quality recognized by the strictest certification from USA and Europe such as REACH, ROHS, FDA, ISO, etc. We will bring customers the best solution for plastic production, so that making customers believe that using masterbatch from US Masterbatch is your advantage in competition.









